Data integration workflows make it possible to leverage disparate datasets to gain value and insight for Esri users. Thousands of data formats and systems exist in order to represent information in specialized ways—ArcGIS has a different set of capabilities than a content management system, which is different from CAD software, which is different from a database management system (DBMS), and so on. The power lies in combining these disparate types in sophisticated, automated workflows. Here are some example data integration workflows:
- Validate data from Survey123 whenever a survey is submitted, integrate it with Cityworks, and email a PDF report to stakeholders.
- Blend geometry and attributes from ArcGIS, Revit, and satellite imagery to create an interactive 3D model of a job site.
- Process Mobile Geodatabases in real time, update the master SQL database, and send a subset of the data to ArcGIS Online to enable end users to see live updates.
- And a lot more examples that we’ll explore below!
This blog focuses on building data integration workflows using FME, the technology that powers the ArcGIS Data Interoperability extension offered with ArcGIS Pro and ArcMap. While the Data Interoperability extension includes Spatial ETL tools for geoprocessing, including data validation, transformation, and translation, FME is a full data integration platform that includes workflow authoring and automating.
Both the FME Platform and the Data Interoperability extension enable users to build powerful data integration workflows. Let’s look more closely at how data integration workflows can help Esri users get more value from their data.
Some of the functionality offered by the ArcGIS Data Interoperability extension and FME.
Data Integration Examples for Esri Users
Here are 5 inspiring examples that inspire us too.
1. Bringing non-Esri data into an Esri environment
Integrating other sources into a GIS environment is important for gaining insight and avoiding data silos. For example, users can integrate external databases, rasters, LiDAR, JSON, XML, CAD, Excel, or any other data type, convert it to an Esri format, or enhance existing Esri data with new information. Integration also empowers users to leverage Esri functionality and ArcGIS Online services for any data, even if it doesn’t come from a GIS source.
Inspiring example: Building an Informative ArcGIS Online Dashboard
Health authorities in Norway created an ArcGIS Online dashboard for sharing critical information about COVID-19 cases in the region. Their FME data integration workflow continuously gathers and integrates data from external APIs and loads it into the ArcGIS Online system. The workflow is automated so it keeps the ArcGIS Online dashboard up to date. Learn more about this project by Helse Midt-Norge and Geodata AS
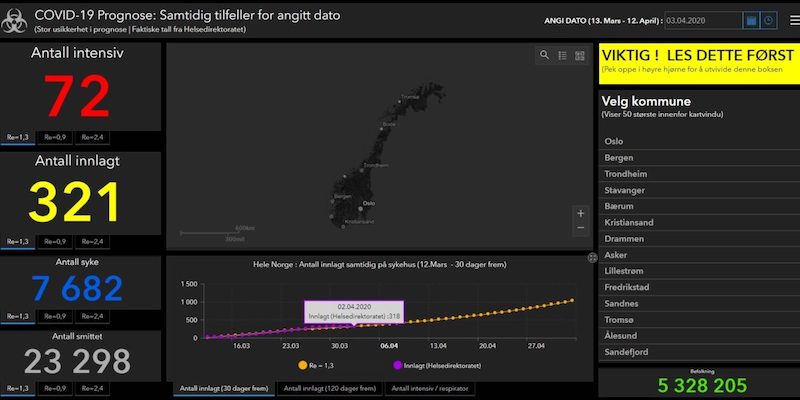
COVID-19 dashboard in Norway powered by Esri and FME. Image from Geodata
2. Making Esri data available to anyone
Converting ArcGIS data into other formats is a key step in making it shareable, informative, and open for collaboration. Data integration workflows make it possible to convert GIS to databases, spreadsheets, business intelligence software, and other systems, as well as make it available in shareable formats like web maps and PDF reports. Many professionals use FME to make their data available in an open data portal.
Inspiring example: Generating Real-Time Survey123 Reports
The City of Delémont created a workflow to generate informative PDF reports from Survey123 data and send them to engineers in nearly real time. When new information comes into ArcGIS Online from Survey123, FME automatically generates a PDF report from the field observations and sends an email with the report attached. Learn more about this project by the City of Delémont and INSER
- See also: How to Make The Most of Survey123 Data
3. Data prep and migration: Moving to, from, and within Esri software
Migration is a fully customizable process with a data integration workflow, as it’s possible to choose which tables, fields, and rows to move, which ones to update, and what event triggers the migration. Many users create workflows to keep multiple datasets and systems synchronized across departments.
Data can also be migrated to the Esri Utility Network or loaded into ArcGIS for Local Government’s Common Information Model by using FME to convert it to the proper structure, format, and standards. Similarly, data can be transformed into the right format for the Esri Community Maps program.
Inspiring example: Creating a Central Repository for GIS and CAD
Comporium created FME data integration workflows to migrate Shapefiles and Microstation DGN files into Smallworld. Merging all of their disparate datasets into one GIS helped them manage their facilities and make better business decisions. Learn more about Comporium’s project
4. Increasing data quality: Performing advanced data transformations
In FME, transformers are tools that power advanced data manipulation, including changing attributes and geometry, performing change detection or CDC, and validating data for completeness, correctness, and standards compliance.
Inspiring example: CAD Validation for Digital Plan Submissions
The City of Henderson created a digital plan submission portal for construction, which involves automated CAD to GIS conversions. CAD data is validated before it is converted to GIS. Learn more about this project by the City of Henderson and Consortech
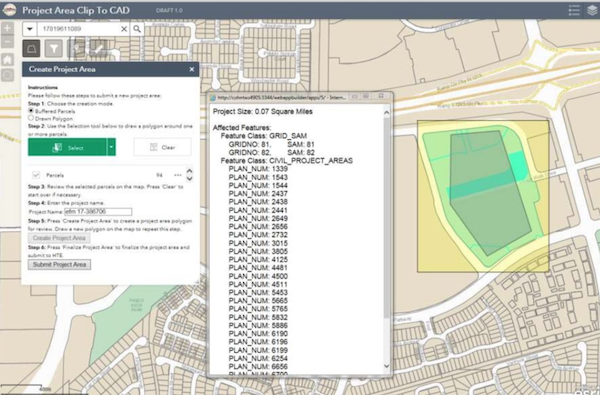
This “clip n ship” interface is part of the City of Henderson’s CAD-GIS integration project that includes automated quality control.
5. Enterprise Automation: Integrating data automatically
Data integration workflows can run on a schedule, in response to an event, or on demand (e.g. as part of a web portal for end users). With the FME Platform, this is achieved using FME Server. With the Data Interoperability extension, Spatial ETL tools can be integrated with other ArcGIS Geoprocessing tools in Esri’s ModelBuilder.
Inspiring example: Building an automated ticketing system
Using ArcGIS Online, Survey123, and FME, the Utah Department of Transportation built a data integration system where suppliers can send e-tickets with asphalt material information, and the data is automatically integrated into the UDOT Geodatabase. This data integration workflow facilitates and standardizes the collection and sharing of materials data for project coordination, documentation, and billing. Learn more about this UDOT project
*
Data integration workflows empower Esri users to connect to any data type and generate more value. Automation is the key to setting up when workflows run, whether the goal is to perform real-time analysis, detect changes whenever new data arrives, or send reports to stakeholders on a nightly basis.
Join us at the upcoming Esri User Conference, July 12-15, 2021, where our FME Experts will be speaking and offering one-on-one meetings in our virtual booth. You’ll also have the chance to attempt our FME-powered escape room! Register today

To learn more about the FME Platform and get started with data integration workflows, visit safe.com/fme.

Tiana Warner
Tiana is a Senior Marketing Specialist at Safe Software. Her background in computer programming and creative hobbies led her to be one of the main producers of creative content for Safe Software. Tiana spends her free time writing fantasy novels, riding her horse, and exploring nature with her rescue pup, Joey.